When reading the success story of any business, the core is the business model. Let us break the term and understand, business model and innovation. A business model is a framework for making money, creating, and capturing value. Innovation is performing tasks differently from the norms. Combined together, a business model innovation is a framework to capture or create value by doing something differently.
Business model innovation does not mean the business has to leapfrog the competition by the product characteristics compared to competitors. A winner in business model innovation is the firm that moved first to change the rules of the game or the firm that came later and pursued a better business model.
To understand business model innovation, it is important to understand the five building blocks of any business model and the type of business model innovation. For better understanding, we have supported each point with relevant examples.
Components of Business Model
Entrepreneurs are well-rehearsed with the components of the business model but do not understand the relevance of the business model analysis. Before we explore each of these components, let us first understand the rationale of each component and the linkage between each of them. To drive customers to the firm, they must provide something worthy to their customer or address the pain points of the customer. The business must provide the customer with a unique value proposition to earn revenue. However, the right value proposition to the wrong customer will not be beneficial, which is why the market segment should be clear.
A revenue model is a structured way to monetize the value proposition. So for the firm to earn high revenue the firm needs to provide the right value proposition to the right market segment. This will intimate the competitors, to prevail during this stage, the firm needs a growth model. The growth model outnumbers competitors and grows profitability. Finally, to deliver the right value proposition, a firm requires the right capabilities i.e. resources, assets, property, human resources, etc.
Customer Value Proposition
A firm’s customer value proposition is the value it can provide the customer through the product/service. It also depends on which aspect solves a problem and/or satisfies the needs of the customer better than the competitors. A value proposition must answer the most asked questions of the target customers: What is so compelling, engaging, rewarding or delightful in a product which will make customers shift from the competitors?
Customers do not always know what they need in a product/service.
For example – customers didn’t know they needed a touch screen and internet connectivity in their mobile phones until the iPhone was launched. The value proposition will also introduce customers to their own latent needs from the product/ service.
The value proposition depends on the reputation, image, assets the firm control, and the relationship with customers.
For Example – A car enthusiast would buy a car not only because of its features and engine capacity but also because it is a BMW or a Ferrari. A brand-focused customer may buy a product because it is sold in a particular store rather than any other store.
Market Segment
The primary source of revenue is through customers and the firm needs to know their customers properly to be able to serve them. Some details which are needed of the customers are:
- What does our primary target audience need?
- What is the market size of our audience?
- Are they willing to pay for your product?
- Will your product be profitable to these target audiences?
The market segment is the section of people to whom the value proposition is being offered or will be offered. The market segment of a business model is about the quality and quantity of the competitors i.e. suppliers, competitors, customers, complementors and others who have to cooperate to create or capture value.
Segmentation can be the type of customers and their preferences, types of products being offered, willingness to pay, demography, geography, distribution channel, types of relationships with customers. Segmentation creates market segments such as a niche market, mass-market, and multi-sided market.
The multi-sided market is when two or more types of market segments are interrelated and the firm makes money by facilitating the interaction.
For example – a credit card market is a multi-sided market as cardholders are on one side and the merchants on the other. The more the cardholder owns a particular card, the better off will be the merchants who accept that particular card and better off will be the credit card company.
Revenue Model
The revenue model component is to get the maximum number of market segment who like the value proposition to pay for the product as close to their reservation price without driving them away. A customer’s reservation price is the highest price a customer is ready to pay for the product. These are some of the types of revenue model:
- Advertising
- Razor-blade
- Brokerage
- Subscription
- Freemium
- Leasing
- Licencing
- Asset sales
- And many more
For example – traditionally Kodak used this technique to sell its film-based camera. They kept the camera cost low whereas the cost of each film was high. This made Kodak popular and they reached record-breaking profits. However, the firm failed miserably when it applied the same model in digital photography.
The price is such an important factor for the revenue model, the entrepreneurs must keep in mind to set the price right. Too high a price will drive the customers away to the competitors or too low a price (without any strategic motive) will lave unnecessary money on the table.
Growth Model
The growth component of a business model is to analyze the following questions and plan them to create the best strategy to grow profitably:
- What a firm has to do to increase the number of customers?
- Strategies to increase the willingness to pay?
- How to keep the price close to the reservation price while keeping it low?
As the firms start providing value for money and making revenue, the competitors increase the prices. The supplier will charge extra money for the commodity or the delivery logistics will increase the charges. This forces the firms to decrease the quality of the product to increase the number of delivery.
Even the competitors will want to go ahead of the firm by imitating or will leapfrog the firm for their benefits, forcing the firm to lower the price or raise its costs.
For example, The internet disrupted the business model of many newspapers and other traditional media, killing their revenue model. Similarly, in today’s world, several unique online business ideas are disrupting the offline business models. An important part of the growth model is to find new UVP and revenue models to relative competitors.
Capabilities
Capabilities are the central point for any business model analysis. The biggest entrepreneurial challenge is to build the capability to take advantage of any opportunity by offering the maximum value proposition. Find the market segment whose needs it can satisfy, increase the number of high-willingness to pay customers in the already existing market or move to the new market. Looking for a better revenue model or improve the existing, work on better pricing model or work towards profitable growth.
Capabilities in a business model consist of resources and activities. Resources are the assets that a firm owns or has access to, whereas activities are what it does. Activities transform resources into values created and/or captured. The quality of the resource determines the amount of value created and/or captured.
For example: At the core of Google’s business model are search capabilities that enable it to deliver searches that are perceived as very dependable by many customers, software that enables it to serve the needs of the long tail searches, tools that it offers to app developers, and so on and so forth.
Conceptualize or Evaluate Your Business Model Framework
Business Model Innovation and its Types
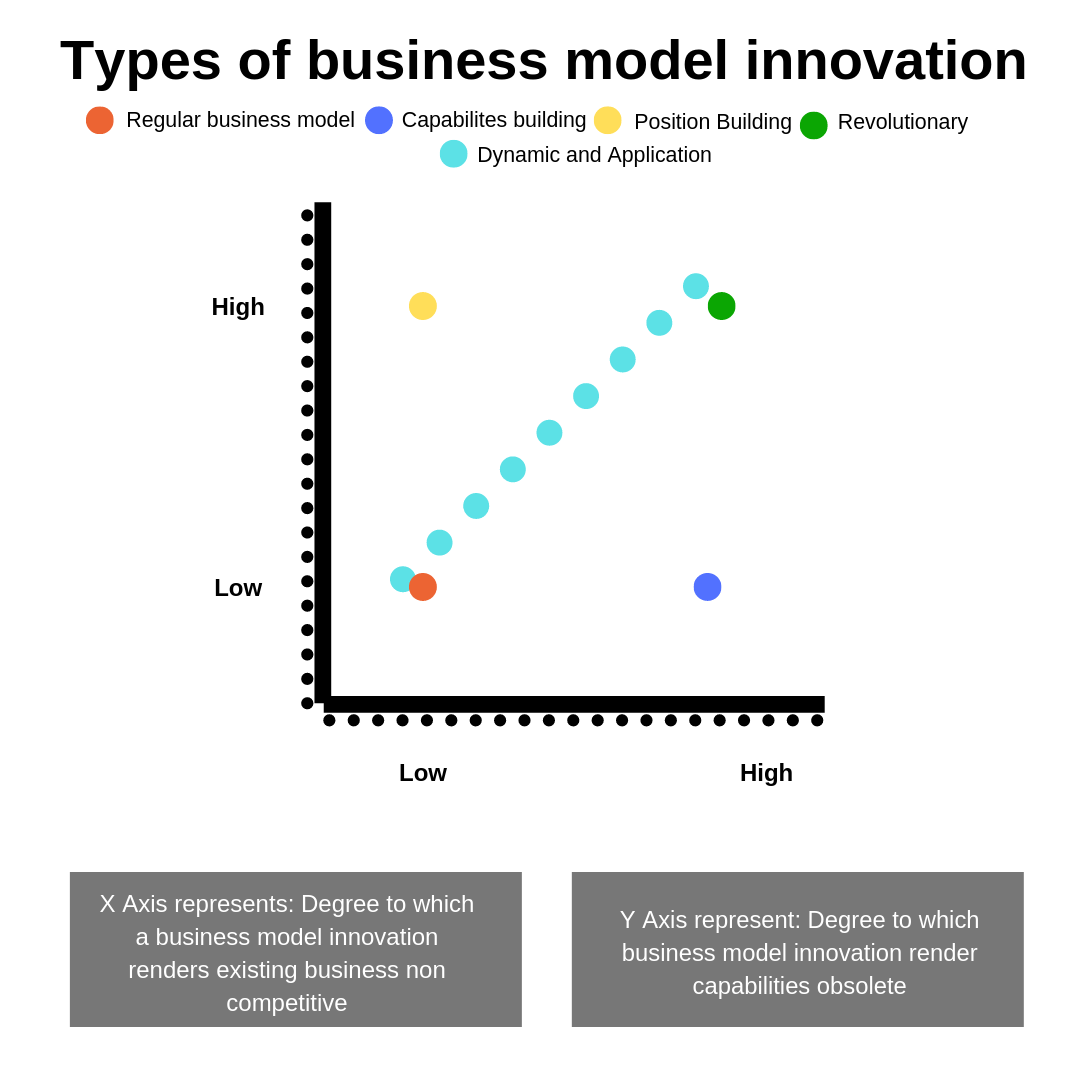
Regular
In a regular business model innovation, the new firms use the same/existing capabilities i.e. value chain activities and underpinning resources. The business model is such that the existing firms in the market still remain competitive. Products of the old firm still take up enough market share to be competitive enough.
Example:
The strategy pursued by Dell in the 90s when it introduced the built-to-order direct model. Rather than passing their product through distributors, Dell directly sold their products to the customers. The customers could order from Dell, informing them about their specification needed by them. Dell brought something new in the market but the capabilities that it used for this strategy was not radically different from the ones existing in the market. The business model was such that the other computer makers like HP, Compaq who sold through distributors were still in the market and earned profitability.
Capabilities Building
In capabilities building innovation, the capabilities needed in the new business model is radically different from the old business model. The old business is still competitive along with the new one. The capability needed in the new business model has to be created from scratch or acquired in some other way.
Example:
A firm that produces renewable resources is an example of capability building innovation. The capabilities of this firm will be highly different from the petroleum-based business model. Creating ethanol from sugar cane, sugar beet, corn and sweet potato which is completely from drills, pump out, refine petrol. Both the fuels co-exist in the market.
The popular example of capabilities building is of brick and mortar vs online store. The capabilities needed for both are completely different yet they co-exist in the market share.
Position Building
In Position building business model, the product/service rooted in the new business model overpowers the product/service in the old business model leaving the latter non-competitive. However, the capabilities of both business models are the same.
Example:
When Walmart came to a small town in the US, it was a position building business model. The capabilities of Walmart were almost the same as retailers’ business models. Walmart rendered many small businesses out of competition as the old business model could not offer the customer the cost-saving offered by Walmart.
Revolutionary
In the revolutionary business model, the core capabilities that underpin the new and old businesses are completely different. The capabilities used by the old business model is completely useless for the new business. The revolutionary business model redefines the creation and capturing of value by overturning the way value chain activities were performed earlier. The rule of the game is changed both market-wise and capability-wise.
Example:
eBay was launched on a revolutionary business model. The online auction required radically different capabilities as compared to an offline auction. For many products, the offline business model is not competitive.
Dynamic and Application
While dividing the business model into different types, we have assumed that the business model is static- that is when a business model is regular it will remain regular always. Nullifying the assumption, many business models may start off as regular but as time goes by many change into position building, capability-building, revolutionary, etc.
Example:
Usually, disruptive technologies start off as regular and move on to become revolutionary or position building. Google was neither the first to introduce a search engine nor the first to launch sponsored ads. However, due to its business model innovation, it became revolutionary and monetized more by being a search engine.
Conclusion
To what extent is the game changed by business model innovation? This one question’s answer must be clear in the mind of entrepreneurs after this post. Understand the two variables in the two by two matrix figure(1.1), after deep analysis of your business and the market in which you are entering. Devising a business model must be done after close consideration of all the points mentioned above. Have other queries related to business model Analysis? Talk to our experts.
Safeguard your Investment Decisions with Our Business Strategy Consultation Services



